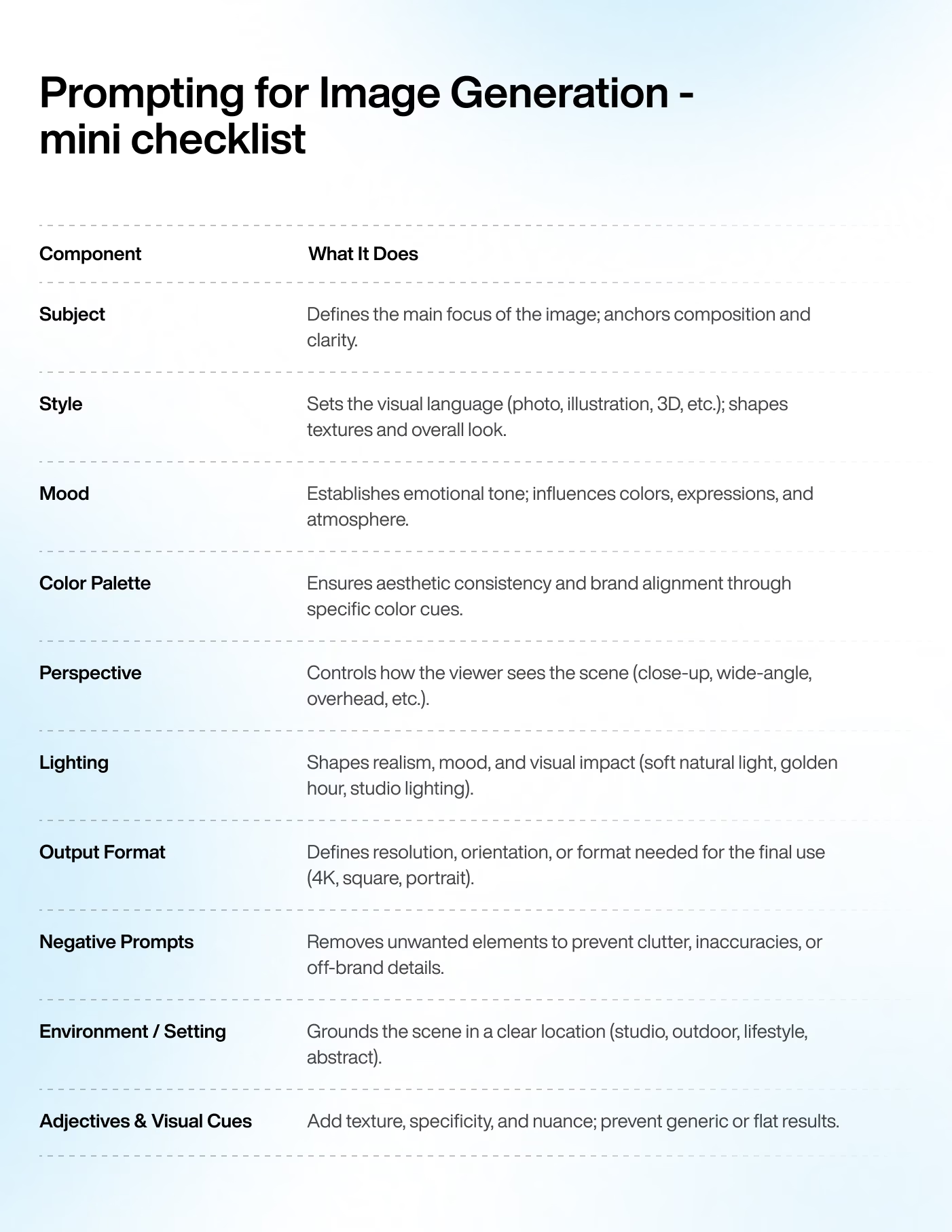
When working with text-based AI models, the quality of your output depends entirely on how clearly you define the task. A great text prompt gives the model direction, context, and boundaries – just like a detailed creative brief does for a writer. Anthropic's prompt engineering overview for Claude highlights the same pattern: be explicit about role, audience, format, and success criteria if you want outputs that are reliable and on-brand.
In this section, we'll break down the key components of an effective text prompt: defining the right persona or role, giving the model a clear task, providing rich context, setting format and constraints, adding examples or references, and finally, refining the output through an iteration loop.
Each element builds on the next. Together, they form a reliable framework for producing accurate, high-quality, and on-brand content at scale.
Persona/role
Every piece of writing starts with a perspective. In AI prompting, that perspective comes from defining a persona or role. Telling the mode who it is shapes how it thinks, speaks, and prioritizes information. It's a simple addition that can completely change the tone, structure, and depth of the output.
Personas also help manage complexity. For example, a journalist persona will write more factually and with curiosity, while a creative director persona will focus on storytelling and visual flair.
By defining that perspective upfront, you reduce back-and-forth editing and get closer to your desired result on the first try.
Example 1: Senior Content Marketer Persona
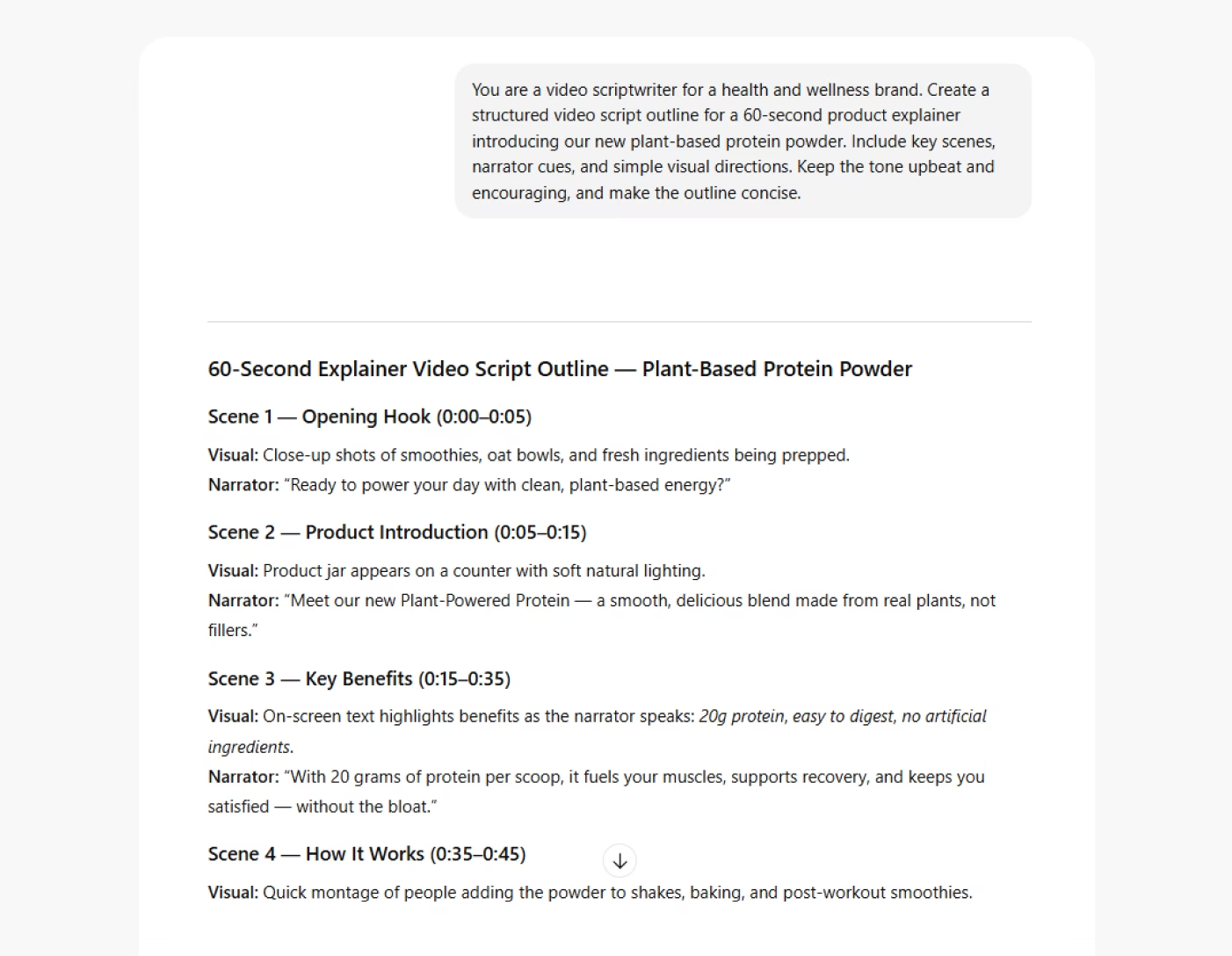
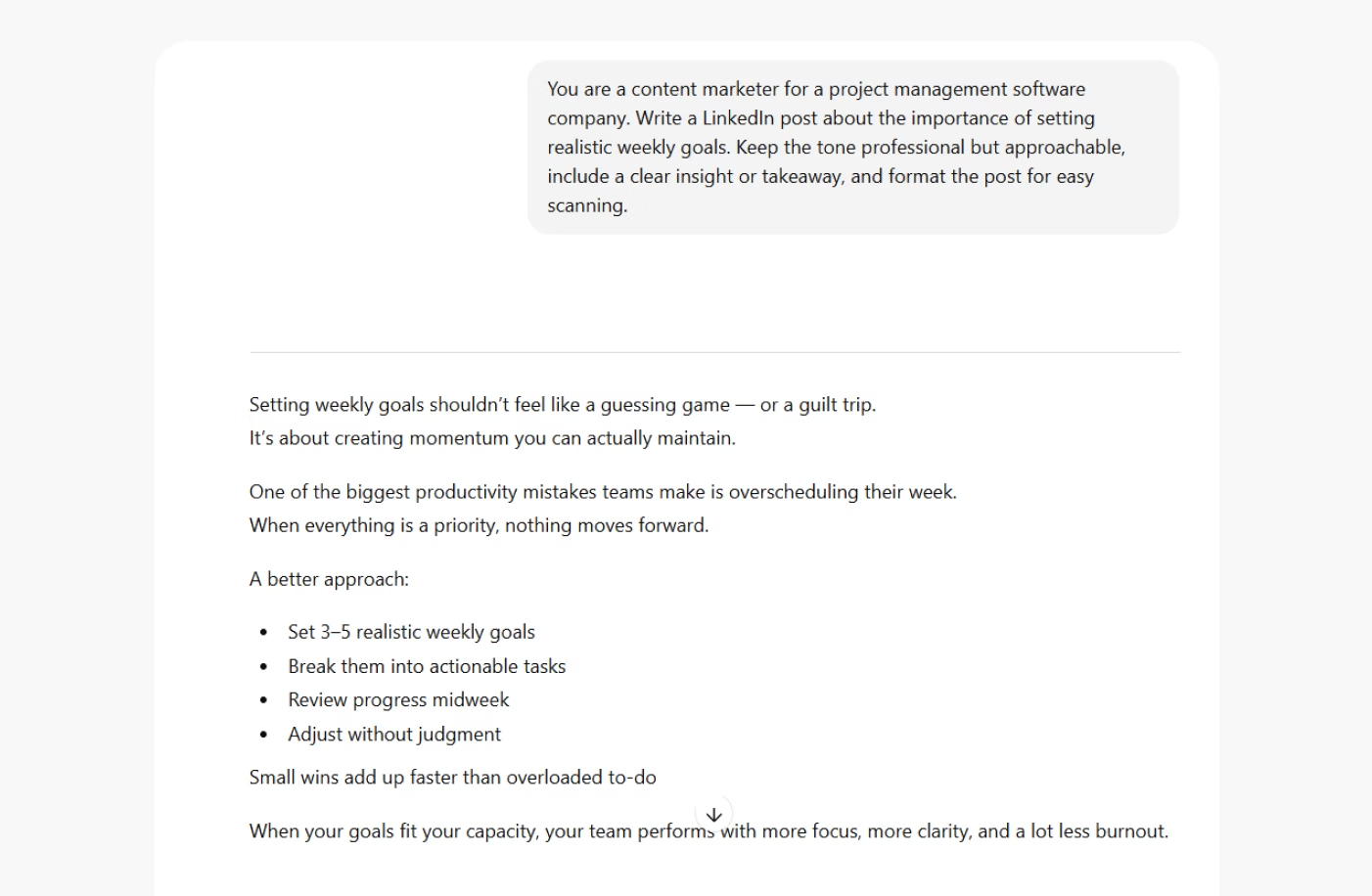
Prompt example: You are a senior content marketer for an eco-friendly fashion brand. Write a LinkedIn post announcing the launch of a new sustainable clothing line.
This persona nudges the AI to focus on themes like sustainability and community. The tone becomes professional yet relatable, and the output is likely to emphasize product benefits through the lens of brand purpose and audience connection.
Example 2: Data-Driven Growth Marketer
Prompt example: You are a data-driven growth marketer. Summarize three key marketing insights from the latest campaign analytics report.
Here, the role frames the model to think analytically and prioritize clarity over creativity. The expected output will be structured, concise, and focused on measurable takeaways, which is ideal for reports or internal presentations.
Example 3: Tech Journalist
Prompt example: You are a tech journalist writing for a mainstream publication. Explain the concept of generative AI to a non-technical audience.
This persona guides the AI to communicate complex ideas in plain language. The model will likely use accessible analogies, avoid jargon, and keep the tone informative but conversational.
Task
Once the role is defined, the next step is to clearly state what you want the AI to do. This is the task, the core instruction that tells the model what kind of output to produce. A well-written task is specific and actionable. It removes ambiguity, ensuring the AI understands the format, purpose, and intent behind your request.
Being too broad can lead to unfocused results. A precise task helps the model narrow its scope and deliver relevant, structured content. Clear tasks reduce the need for multiple revisions and make the AI more efficient as a creative partner.
Example 1: Blog Outline Task
Prompt example: Write a 1,200-word blog outline about how small businesses can use AI tools to improve customer engagement.
This task gives the AI both a topic and a clear deliverable. You can expect a structured response that includes sections, logical flow, and potential talking points. It's going to be ready for further expansion into a full article.
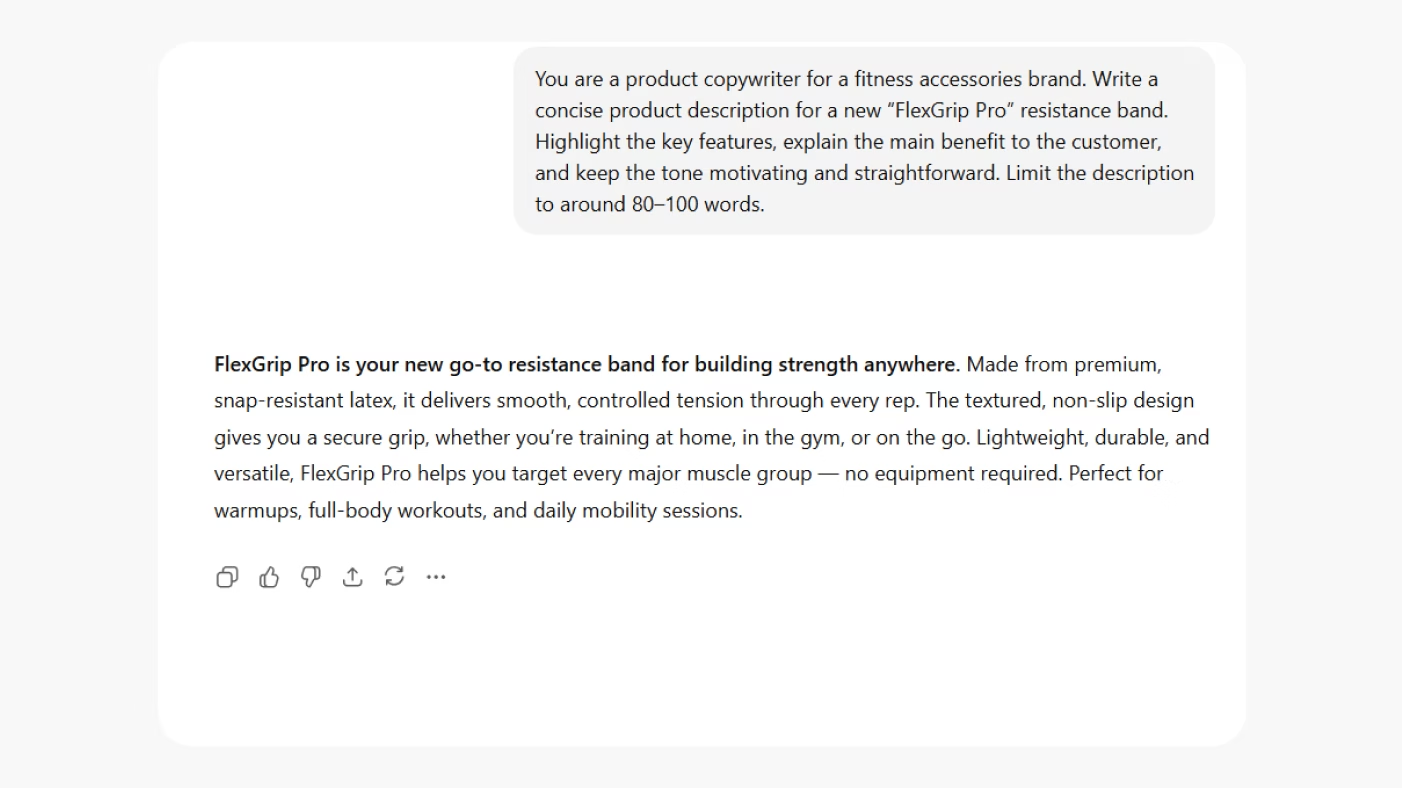
Example 2: Product Description Task
Prompt example: Write a 100-word product description for a new noise-cancelling headphone mode designed for frequent travelers.
Here, the task defines the format, length, and focus. The AI will likely produce concise, benefit-driven copy that highlights features and value, making it easy to drop directly into an e-commerce page.
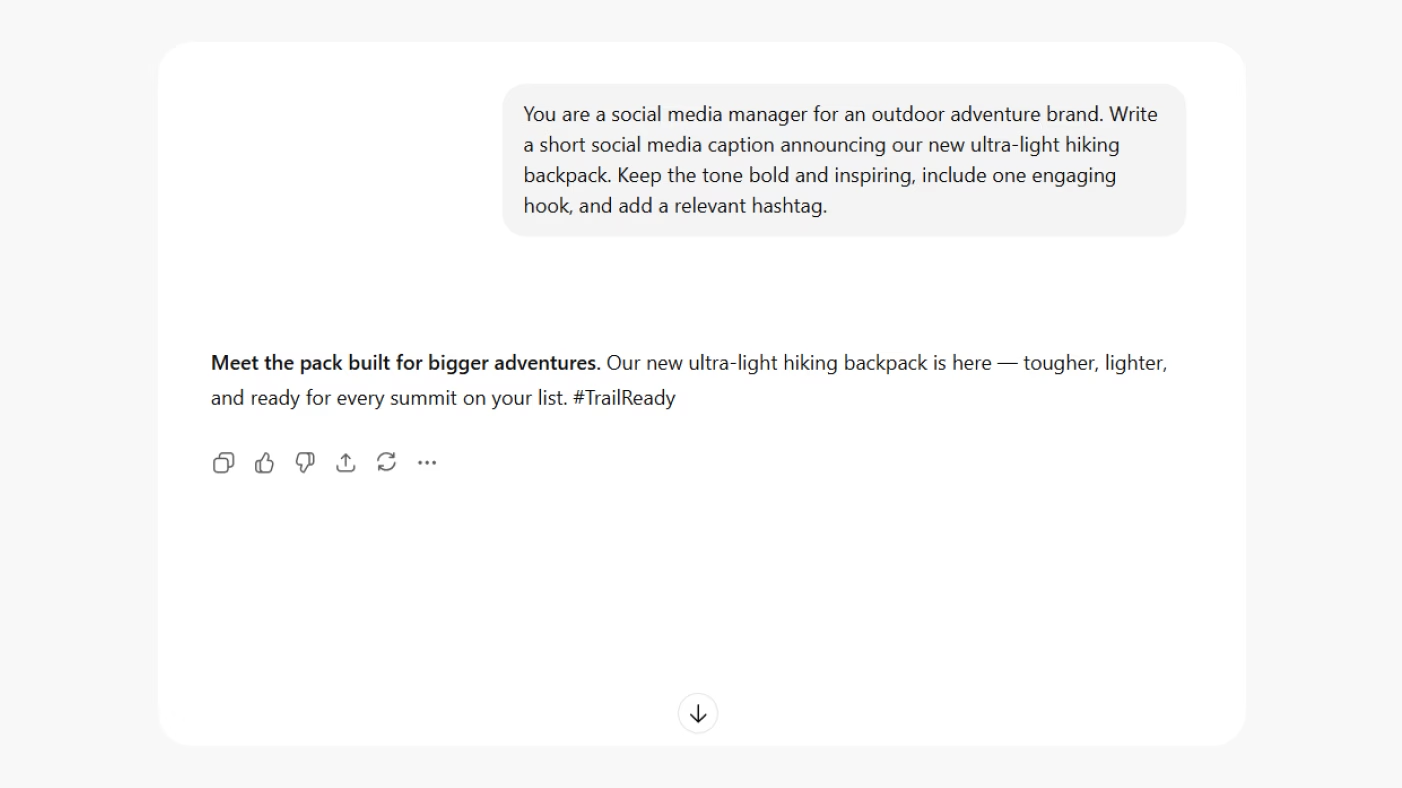
Example 3: Social Media Post Task
Prompt example: Write a short Instagram caption announcing the launch of a limited-edition summer drink collection.
This task guides the AI to create content that's short, engaging, and optimized for social platforms. The model will likely emphasize tone and emotion – something fun, punchy, and shareable.
Context
If the task tells the AI what to do, the context tells it how and why. Context provides the background information the model needs to deliver relevant, on-brand, and goal-oriented results. It includes details such as your brand voice, audience profile, key message, product information, or even snippets of past content.
Without context, the model fills in the blanks with assumptions – often producing generic or off-brand output. Adding a few lines of background dramatically improves accuracy and tone. It helps the AI mirror your brand identity, reflect your priorities, and stay aligned with the purpose behind the content.
Example 1: Brand Context for a Blog Post
Prompt example: You are a senior content marketer for an eco-friendly fashion brand. Write a 1,200-word blog post about the future of sustainable materials.
Context: The brand targets eco-conscious millennials who value style and ethics equally. Our tone is optimistic, informative, and forward-looking.
This context helps the AI balance authority with accessibility. The model will likely highlight innovation and environmental impact in a way that connects emotionally with the target audience.
Example 2: Audience Context for a Newsletter
Prompt example: Write an introductory paragraph for a newsletter about productivity tools.
Context: The audience is a mix of startup founders and freelancers looking for practical, time-saving tips. Keep the tone friendly, relatable, and professional.
The added audience context shapes both tone and vocabulary. The AI will likely produce a conversational opening that feels personal yet credible, setting the right tone for a business-oriented readership.
Example 3: Data Context for a Press Release
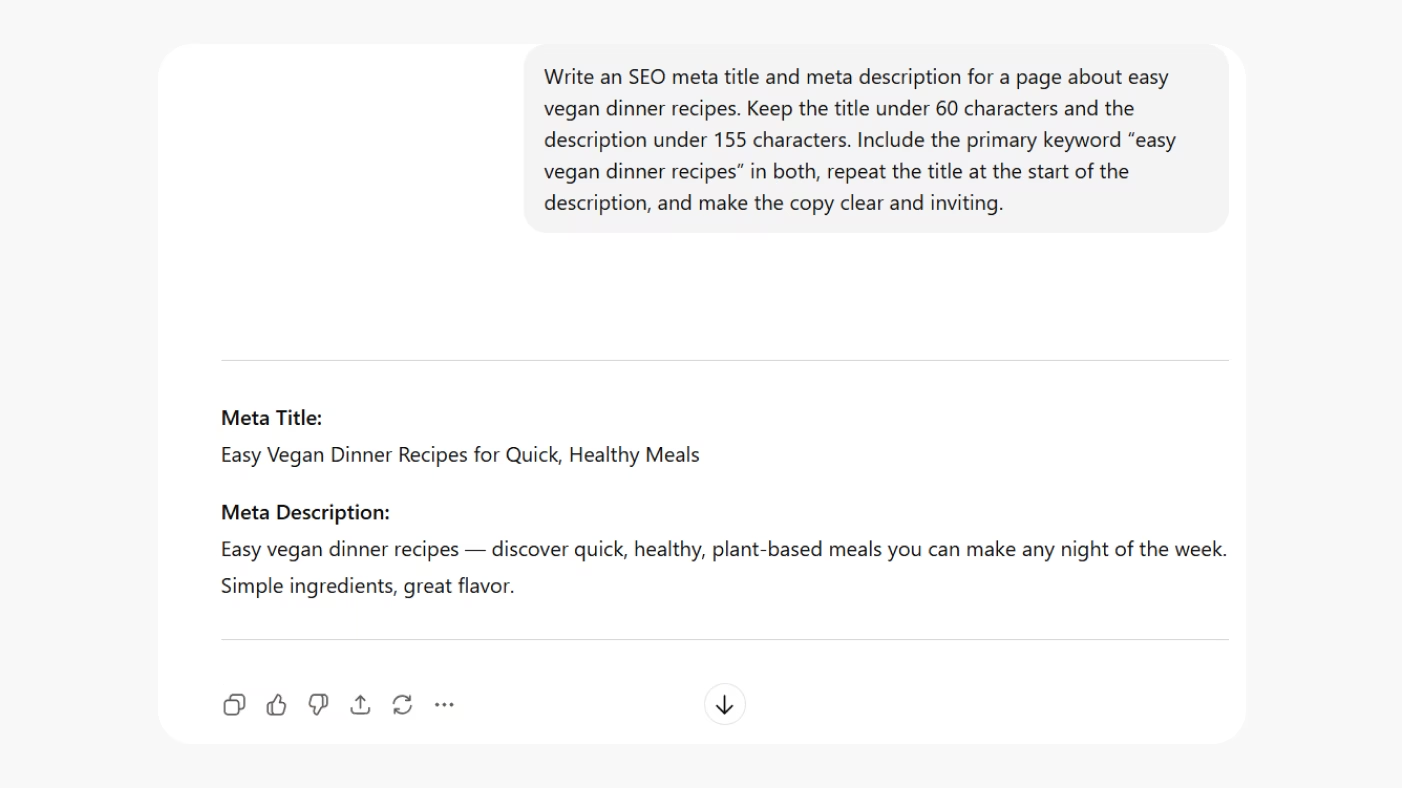
Prompt example: Write a 300-word press release announcing our company's record-breaking Q4 results.
Context: Revenue grew 40% year-over-year. Customer satisfaction reached 92%. The company expanded into two new markets. Maintain a confident, professional tone suitable for media distribution.
Here, the context gives the AI concrete data and desired tone, which results in a polished, fact-based release. Instead of vague claims, the output is more likely to include compelling proof points and business impact.
Once you've defined the role, task, and context, the next step is to tell the AI how you want the output delivered. Format and constraints define the structure, tone, and boundaries of the response. They include elements such as length, style, layout, and specific formatting requirements.
Example 1: Structure Format for a Blog Outline
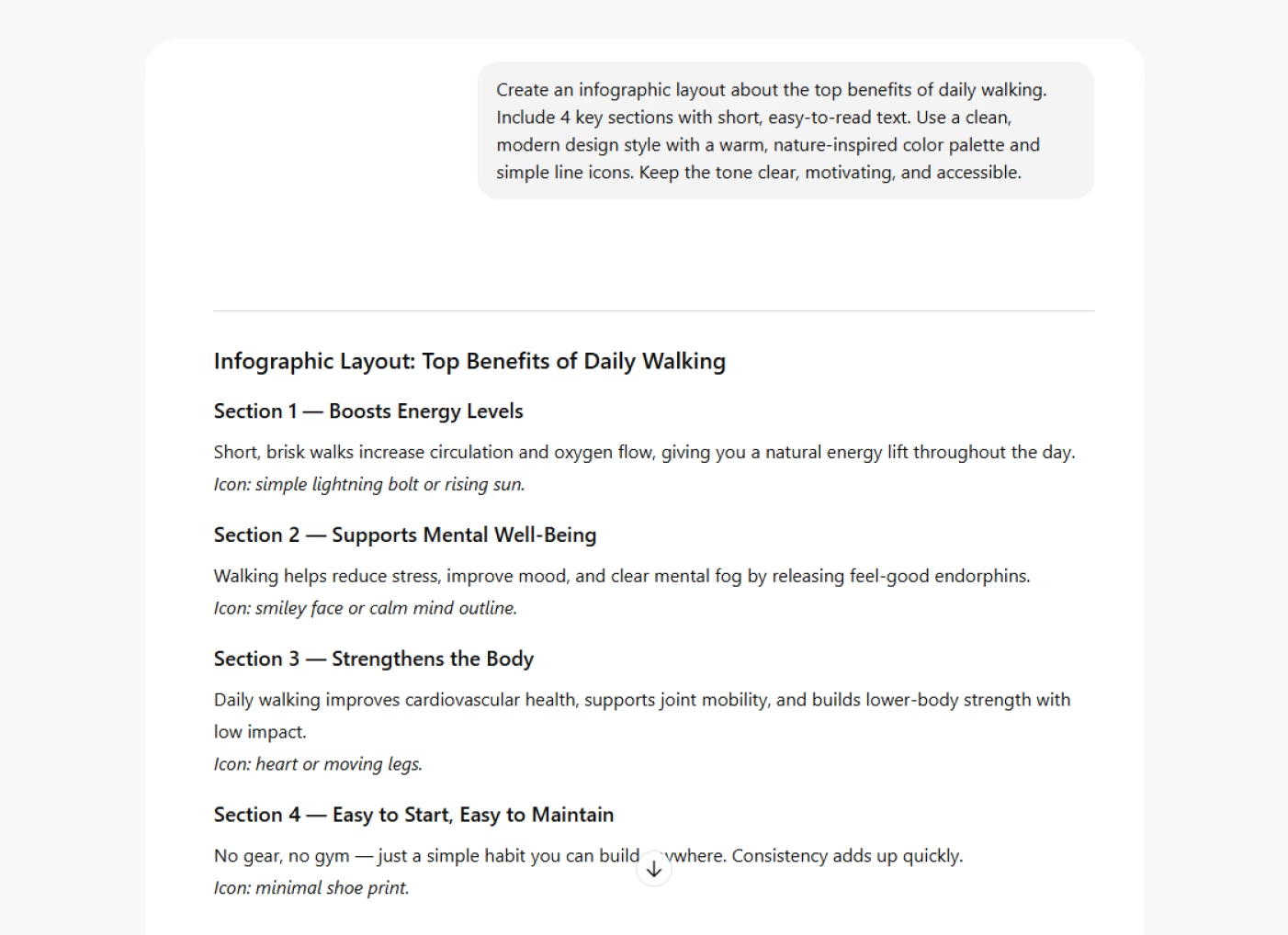
Prompt example: You are a senior content strategist. Create a blog outline about AI-powered customer service tools.
Format and constraints: Use clear section headings (H2 and H3). Include brief descriptions under each, and limit the outline to 400 words.
This structure encourages the AI to produce a concise, well-organized outline. The format instructions ensure the output can be used directly for planning or content production without heavy editing.
Example 2: Tone and Style for Social Copy
Prompt example: You are a social media manager for a coffee brand. Write three short X posts promoting our new cold brew line.
Format and constraints: Keep each post under 280 characters. Use a playful tone, and end with branded hashtags.
The format rules keep the AI within platform limits and ensure a consistent tone. You can expect catchy, short, and fun brand-aligned messages.
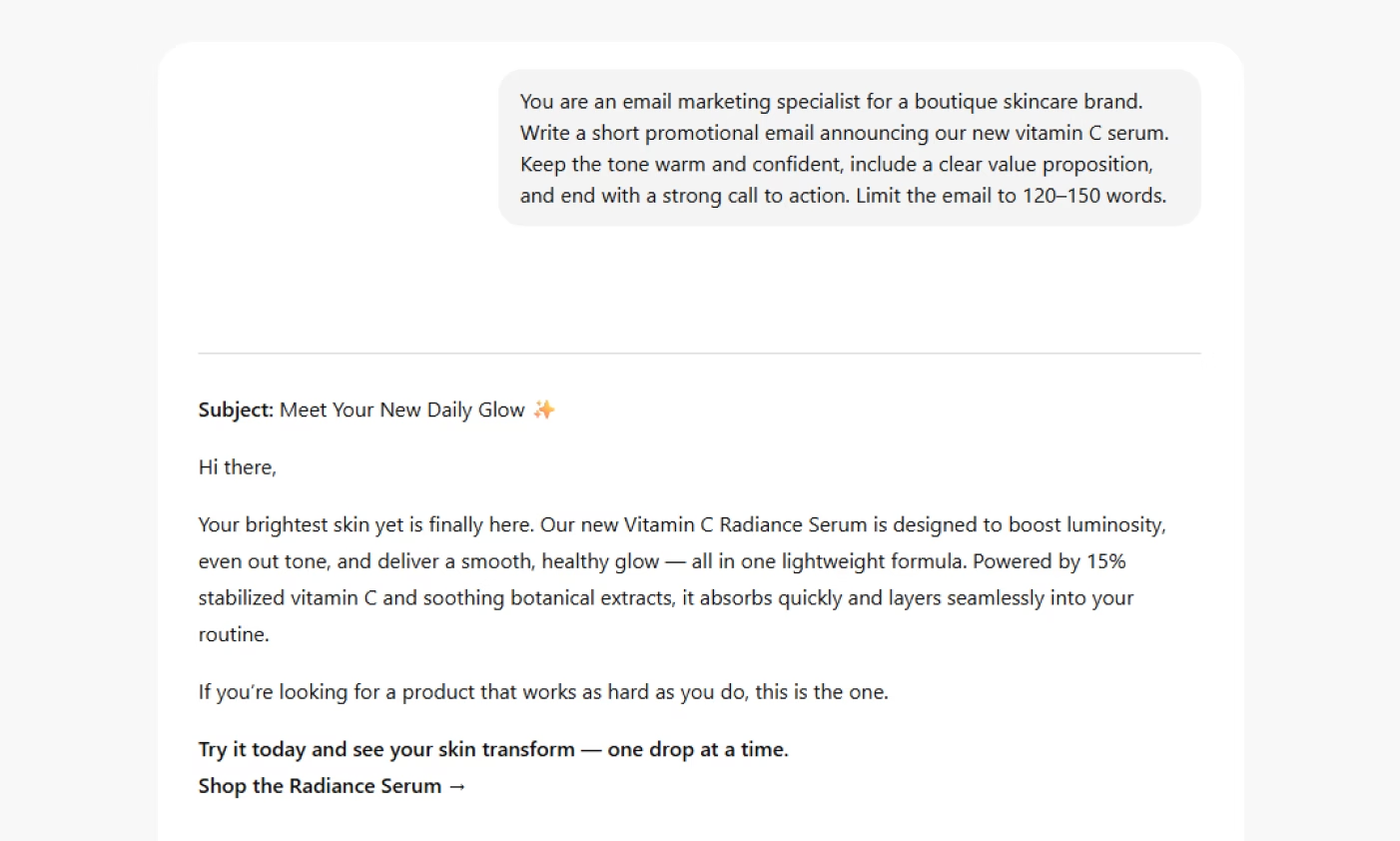
Example 3: Length and Voice for Email Marketing
Prompt example: You are a copywriter working in a tech company, and you need to write an email. An email should announce a new product launch.
Format and constraints: Limit to 150 words. Maintain a friendly, yet professional tone. Include a clear call to action.
By setting limits, you help the AI stay concise and on point. Expect an email that feels lively, easy to read, and built to make readers click
Examples / References
One of the most effective ways to guide an AI model is to show it what "good" looks like. Examples and references act as creative anchors. They demonstrate tone, structure, or style, helping the model understand the standard you expect.
In this part of your prompt, you can include sample sentences, past brand content, or tone guidelines that define what's in (and out) of scope.
Example 1: Tone Reference for Writing a Blog
Prompt example: You are a senior content writer who works in a marketing agency. Write a blog introduction about why storytelling improves brand engagement.
Reference: Use a tone similar to Recommend's blog: clear, human, and smart.
By referencing an established brand voice, you help the AI mirror a specific writing style, which it excels at.
Example 2: Structural Reference for Case Studies
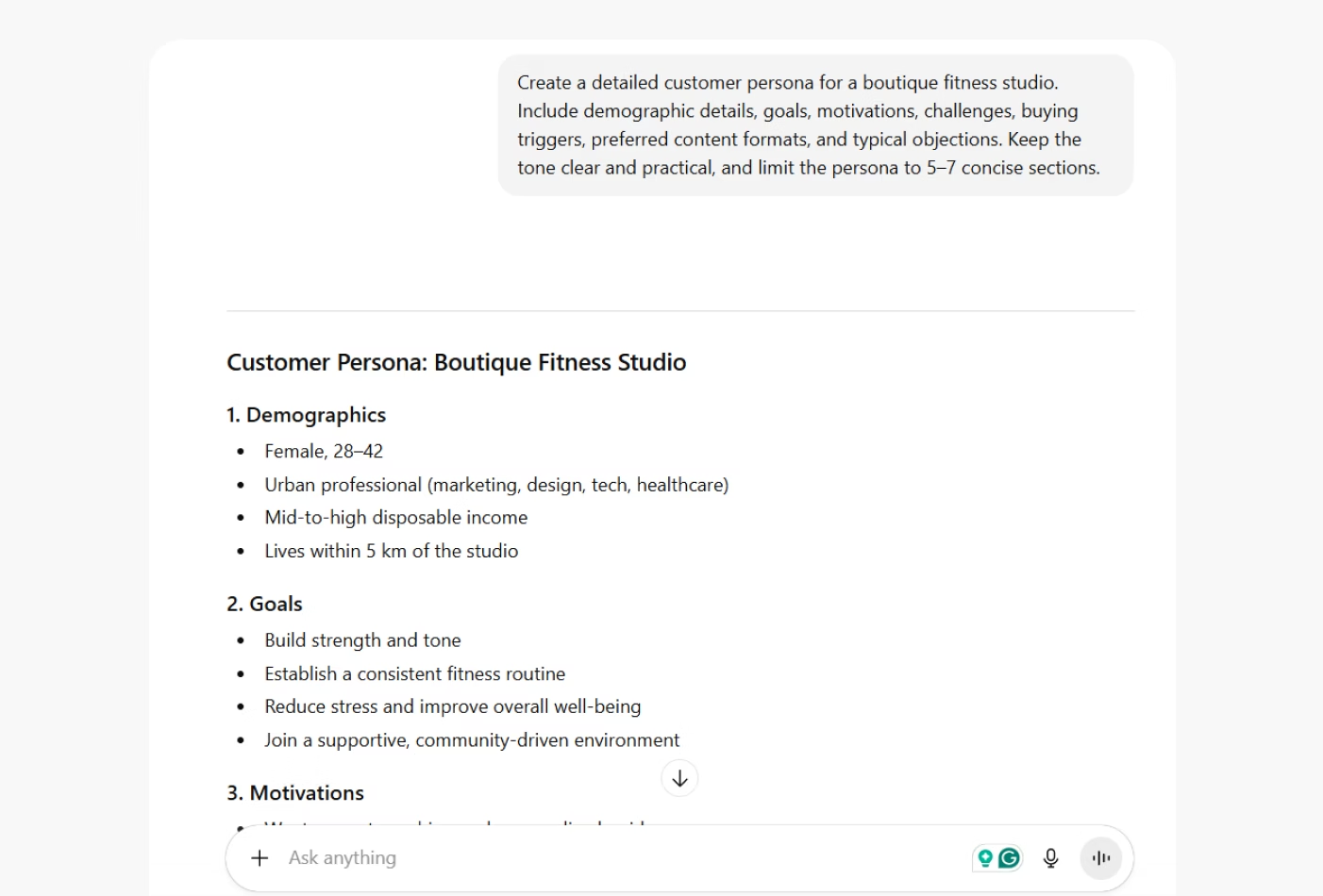
Prompt example: Write a one-page case study about a company that used AI to reduce content production time by 40%.
Reference: Follow this structure: challenge → approach → results → takeaway.
Here, the example provides a ready-made framework. The AI will organize the content logically, keeping it focused on outcomes and ensuring the result fits professional business formats.
Example 3: Style Reference for Social Copy
Prompt example: You are a social media manager for a travel brand. Write three Instagram captions about summer destinations.
Reference: Match the tone with our winter campaign. Make it warm, adventurous, and emotionally engaging.
This kind of brand reference ensures continuity across campaigns. The AI will pick up on emotional cues and phrasing patterns, helping the new posts sound cohesive and instantly recognizable.
Iteration / Feedback Loop
Even the best prompt rarely gets it perfect the first time. That's why iteration – refining your prompt based on feedback – is one of the most valuable parts of the prompting process. Each round helps you clarify what works, adjust what doesn't, and move closer to the result you actually need.
Think of it as a conversation, not a command. When you give the AI targeted feedback, the model learns your intent and fine-tunes the output. Over time, this back-and-forth becomes a repeatable workflow that consistently produces better, faster results.
Iterative prompting isn't just a safety net: it's a best practice.
Example 1: Refining Tone and Clarity
Prompt example: Write a short product description for our new smartwatch.
Follow-up prompt: The tone feels too technical. Make it more lifestyle-focused and highlight the benefits for everyday users.
By giving clear, targeted feedback, you steer the AI toward a tone that better fits your audience. The next version will likely feel more human and approachable.
Example 2: Expanding Depth and Detail
Prompt example: Write a blog intro about the importance of sustainable packaging.
Follow-up prompt: Add a short stat or research insight to make it more credible and data-driven.
Here, you're not rejecting the output. Instead, you're enhancing it. A small tweak can elevate the content from surface-level to informative, giving to more authority and reader appeal.
Example 3: Optimizing Structure for Readability
Prompt example: Summarize our company's latest quarterly results in 300 words.
Follow-up prompt: Break it into bullet points for key takeaways and keep the language concise.
This feedback directs the AI to reformat rather than rewrite. The result will be easier to scan and more suitable for reports or executive updates.